Why Fourier transform is used in proteomics
in Proteomics
Spectral similarity를 구할 때 왜 Fourier transform을 사용할까?
Fourier transform은 time domain의 신호를 frequency domain으로 바꾸는 변환인데, 주로 time-domain에서의 입력 신호가 주기함수 (periodic function)일 때 매우 유용하다. 왜냐하면, 주기함수의 경우 time domain에서의 복잡한 신호가 Fourier transform을 거치면서 특정 주파수(frequency)의 신호로 분리가 되므로 신호가 단순화되는 효과가 있기 때문이다 (아래 그림 참조, 출처: 위키피디아 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_transform).
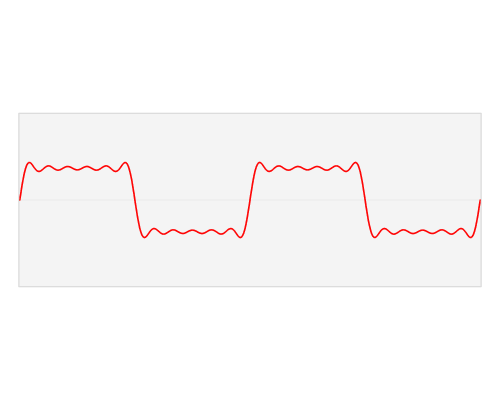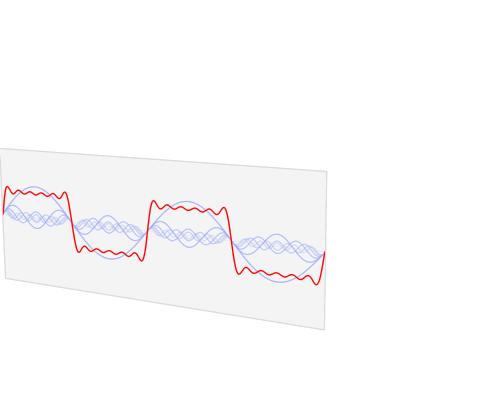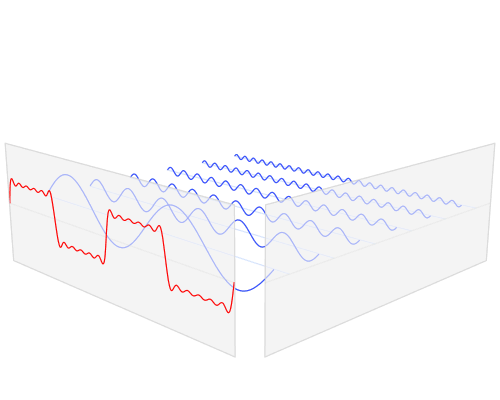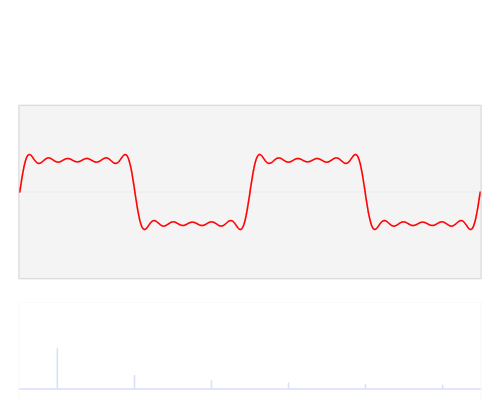
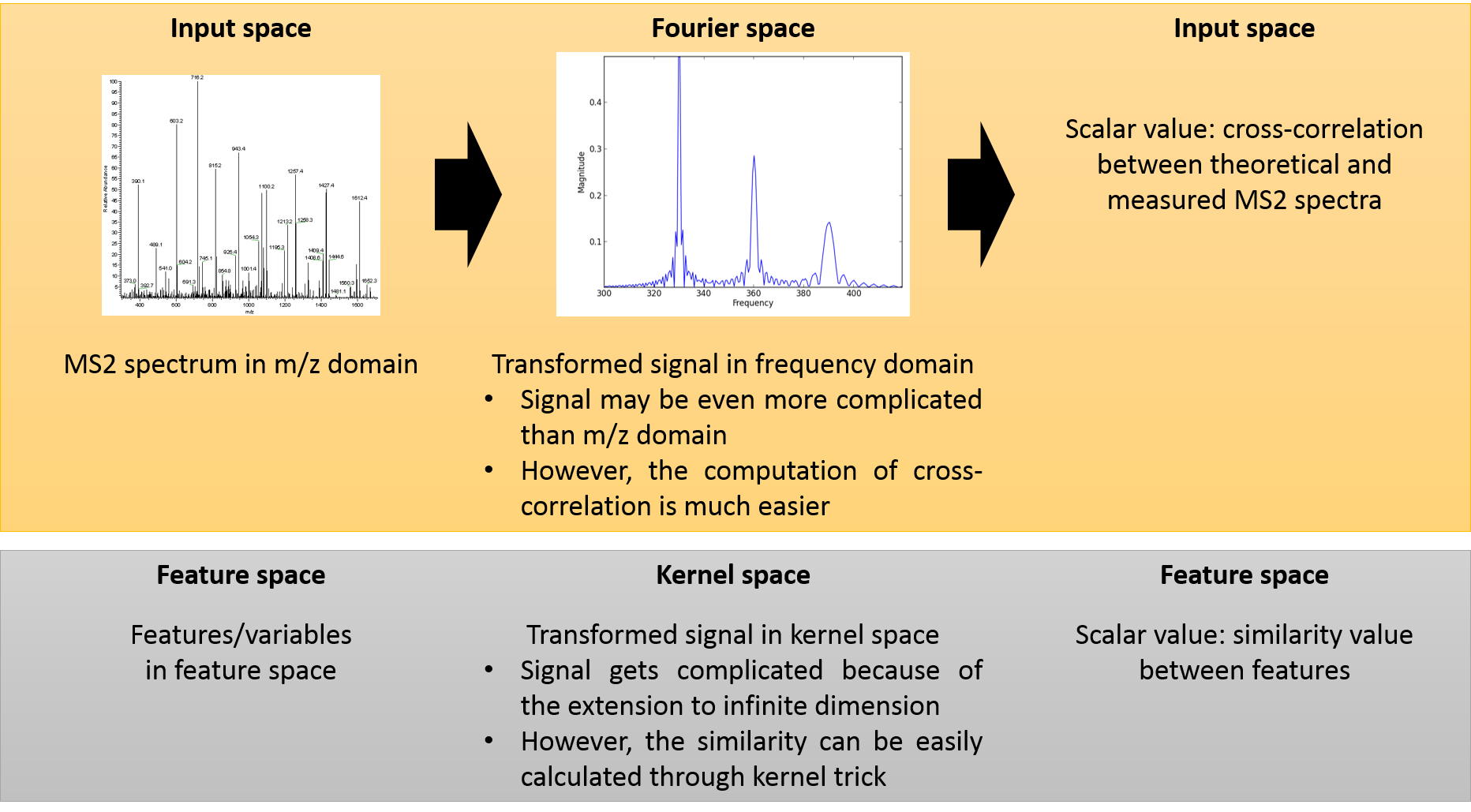
그런데 m/z domain에서 정의되는 MS2 spectrum은 주기함수가 아니므로 Fourier transform을 거칠 경우에 frequency domain에서의 신호가 오히려 m/z domain에서 보다 더 복잡해질 수도 있다. 그럼에도 불구하고 cross-correlation에 기반한 spectral similarity를 구할 때 Fourier transform을 사용하는 이유는 cross correlation의 계산이 frequency domain에서 매우 간단해지기 때문이다.
즉, 신호 자체가 단순화되는 효과는 없지만, similarity를 구하기 위한 계산 절차가 간단해지는 효과가 있기 때문에 Fourier transform을 사용하는 것이다.
이는 kernel machine의 철학(?)과도 유사하다고 볼 수 있는데 kernel machine은 feature space에서의 variable들을 더 복잡한 (infinite dimension을 갖는) kernel space로 transform하고, kernel space에서 구한 similarity measure를 다시 feature space로 가져와서 연산을 수행한다 (아래 그림 참조).